Complex chronic diseases like diabetes, sickle cell anemia, and Alzheimer’s disease are multifactorial conditions, meaning they’re influenced by many factors, such as infectious causes, genetic predispositions, and environmental conditions. This makes them uniquely difficult to treat. Take, for example, Alzheimer’s disease. The neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease is thought to be influenced by four intertwined factors, including A-beta plaques, tau tangles, small vessel leaks, and TDP-43 hardening. Developing therapeutics to treat conditions like Alzehimer’s, which have complex causative factors, is incredibly challenging.
Biologics for Complex Disease
Complex diseases have been challenging to address with chemically synthesized small molecule drugs. Biologics offer new hope. Biologics are large, complex treatment entities that are derived from living organisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or mammalian cells. They target specific cells in the body to stimulate or suppress the immune system. They are typically given through injection or infusion. While biologics can be more expensive than traditional drugs due to the complexity of their production processes, they can also offer significant benefits to patients with complex medical conditions. Examples of biologics include cytokines, growth factors, certain vaccines, cell therapies, gene therapies, RNAi, and monoclonal antibodies, which we will focus on here.
Example: IgG Antibodies
While there are five main classes of antibodies (or immunoglobulins, Ig), the most prevalent is IgG. Although the smallest in size, IgG antibodies are the highest in prevalence, accounting for 80% of total antibodies in serum. They are the main antibody associated with secondary responses that neutralize toxins. As shown in Figure 1, IgG antibodies are made of symmetrical heavy and light protein chains that are shaped like the letter Y, where the base (or constant Fc region) interacts with immune-system components and the two arms (or variable Fab region) recognize and interact with an antigen.
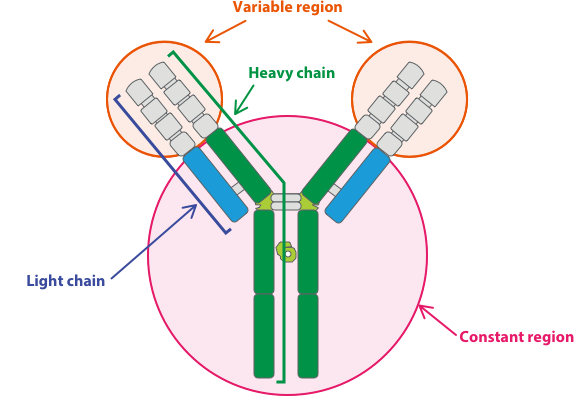
Figure 1: IgG antibodies are made of symmetrical heavy and light protein chains that are shaped like the letter Y, where the base (or constant Fc region) interacts with immune-system components and the two arms (or variable Fab region) recognize and interact with an antigen (Source: https://kkna.kyowakirin.com/what-we-do/research/)
Distinct regions of specific chromosomes control the creation of proteins that comprise an antibody. In humans, chromosomes 2, 22, and 14 all contribute to the creation of IgG antibodies. The antibody assembly process is incredibly complex, with different building blocks, originating from different gene fragments, coming together in a combinatorial fashion. These different assembly combinations may also have junctional and somatic differences, which all results in a tremendous amount of antibody diversity.
Antibody Analysis
Analyzing the impact of therapeutic antibody candidates’ diversity is an essential part of antibody discovery efforts and, for many teams, a key challenge as well.
Take for example, B-cell antibody repertoire analysis. B-cells are white blood cells produced in the bone marrow that play a key role in the body’s immune response to infection. They produce antibodies to help attack foreign invaders, such as by binding to and neutralizing harmful protein (otherwise known as antigens), preventing antigens from entering cells, or marking antigens for destruction by other immune cells. To study B-cell antibodies, researchers must unite, analyze, and re-analyze data data coming from both mass-spectrometry protein analysis (Ig-Seq) and sequence analysis (BCR-Seq) so that they can attain a more complete picture, make the best possible research decisions, and uncover new insights.
While combining and recombining different types of research data and analyses is imperative, it’s also incredibly challenging without a flexible end-to-end R&D platform like Dotmatics Platform that helps discovery teams optimize both dataflows and workflows.
Next Steps
Read more about the ways Dotmatics is supporting research composability and multi-dimensional discovery with a comprehensive and advanced biologics R&D solution.